Why in News?
The APEC Summit 2025 is set to take place in Gyeongju, South Korea, under the theme “Building a Sustainable Future.” This summit is expected to address critical issues affecting the Asia-Pacific region, focusing on sustainable development and economic cooperation among member economies.
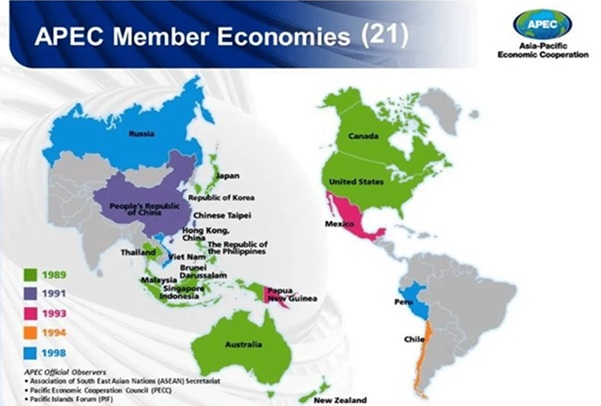
About APEC (Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation)
- Established: 1989
- Headquarters: Singapore
- Members: 21 economies, including the USA, China, Japan, Australia, Canada, and South Korea, which together account for 60% of global GDP and 47% of global trade.
- Nature: APEC operates on a non-binding, consensus-based approach.
- Objective: To promote sustainable economic growth, free and open trade, investment, and regional cooperation.
Key Focus Areas
- Trade liberalization
- Digital economy
- Climate change
- Capacity building
Trade Tensions and Policy Uncertainty
The ongoing US–China tariff war continues to cast a shadow over regional trade dynamics. According to the APEC Report 2025, projections indicate:
- A potential decline in regional GDP growth to 2.6% (down from 3.6% in 2024).
- Export growth is expected to be 0.4%, while import growth may only reach 0.1%.
The uncertainty surrounding trade policies, particularly due to the Trump administration’s tariffs and China’s restrictions on rare earth mineral exports, adds to the complexity of the economic landscape.
Economic Growth and Inclusive Development
The APEC region, which represents 60% of global GDP, is experiencing uneven growth amid signs of a global slowdown. While inflation is easing, investment levels remain weak. The 2025 Priorities include:
- Transitioning to the formal economy (Lima Roadmap 2025–2040).
- Enhancing the participation of indigenous communities in economic development.
Digital Economy and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The APEC Internet and Digital Economy Roadmap (AIDER) is set to conclude in 2025, bringing new challenges to the forefront:
- AI ethics
- Data privacy and governance
- Bridging the digital divide
These issues are critical as economies strive to harness the benefits of digital transformation while ensuring ethical standards and equitable access.
Climate Change and Sustainability
Despite geopolitical tensions, climate issues remain central to APEC’s agenda. The Bangkok Goals on Bio-Circular-Green Economy (BCG Model) continue to guide discussions. Key focus areas for 2025 include:
- Energy cooperation
- Food security
- Supply chain resilience
Reports emphasize that sustainable growth is foundational for regional cooperation, highlighting the need for collaborative efforts to address climate challenges.
Geopolitical Challenges
Regional and global security concerns are increasingly influencing APEC dynamics. Major developments include:
- The Russia–Ukraine conflict
- Ongoing Middle East unrest
- The US–China strategic rivalry
India and APEC
India, while not a member of APEC, has shown consistent interest in joining since the early 1990s. Key milestones include:
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1991 | India expressed interest in joining APEC. |
| 1997 | Formally applied for membership, but APEC imposed a moratorium on new members. |
| 2007 | Moratorium extended for another 10 years. |
| 2012 & 2018 | India renewed its interest, but no decision was made. |
Reasons for India’s Non-Membership
- Geographical Criteria: APEC limits membership to “Asia-Pacific” economies; India is often categorized under the “Indo-Pacific” region.
- Pace of Economic Liberalization: India’s market reforms in the 1990s were slower than APEC’s liberal economies.
- China’s Opposition: China reportedly resisted India’s entry to maintain its influence within APEC.
- Moratorium Policy: Since 1997, APEC has maintained a moratorium on new memberships.
Why APEC Matters for India
-
Regional Economic Integration:
- APEC economies contribute approximately 60% of global GDP and 48% of global trade.
- Membership would provide India access to large, dynamic markets.
-
Boost to Trade and Investment:
- Reduced tariffs among members would benefit Indian exports.
-
Diplomatic Leverage:
- APEC offers a dialogue platform with major economies like the US, China, and Japan.
- Economic Reforms:
- Membership could accelerate India’s trade facilitation, digital trade, and supply chain reforms.
India’s Current Strategy
Although not a full member, India participates as an Observer and in Partner Dialogue mechanisms. The country is strengthening engagement through alternative platforms such as:
- BRICS
- Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF)
- QUAD
- RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership) – indirectly connecting with APEC economies.
Amid shifting trade dynamics and US tariff policies, India is pursuing bilateral trade agreements with key APEC members, notably the UK and Australia, to enhance market access and economic cooperation.